2018-08-24
Team LI Chengfeng, ZHOU Zongquan and others from CAS Key Lab of Quantum Informaiton developed multi-degree-of-freedom (DOF) multiplexed solid-state quantum memory, and demonstrated for the first time photon pulse operation functions with time and frequency DOFs. The result is recently published on Nature Communication.
The faithful storage and coherent manipulation of quantum states with matter-systems enable the construction of large-scale quantum networks based on quantum repeater. To achieve useful communication rates, highly multimode quantum memories will be required to construct a multiplexed quantum repeater.
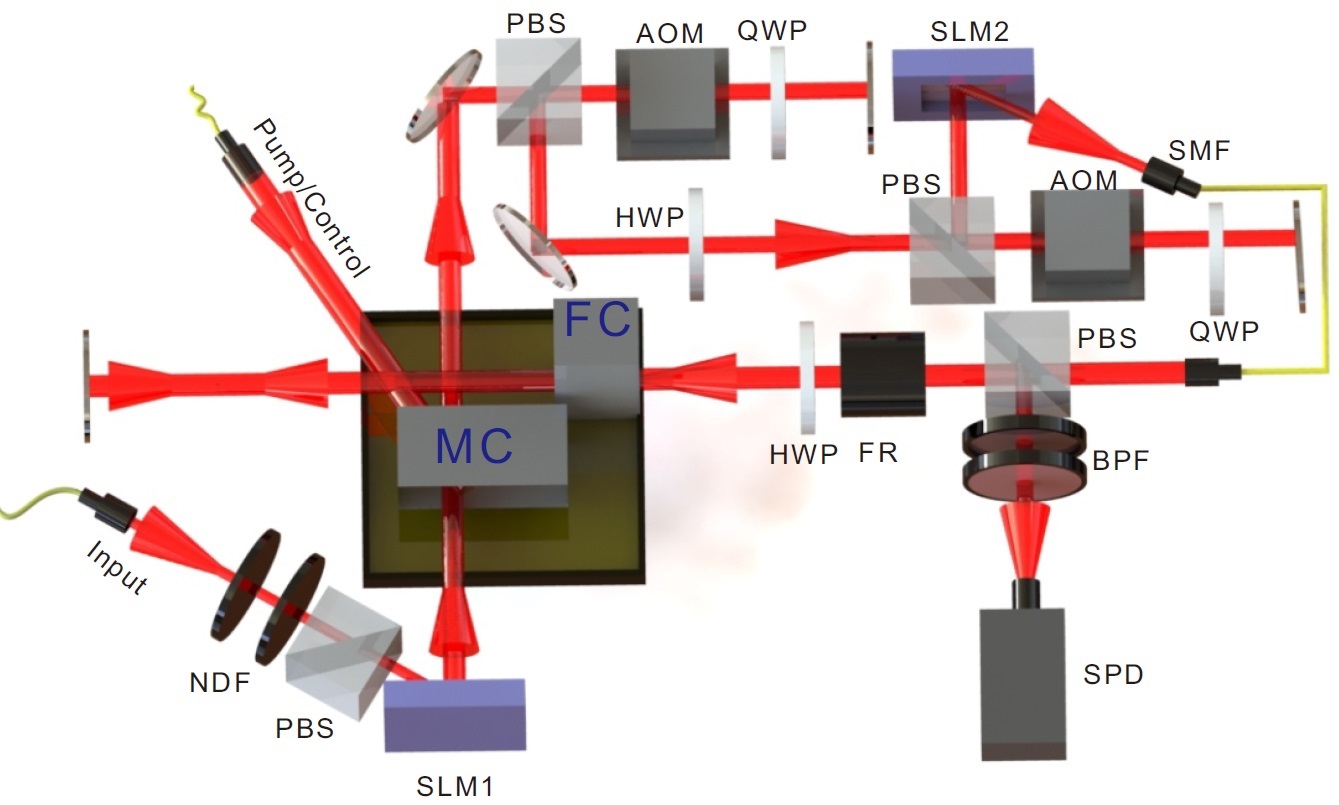
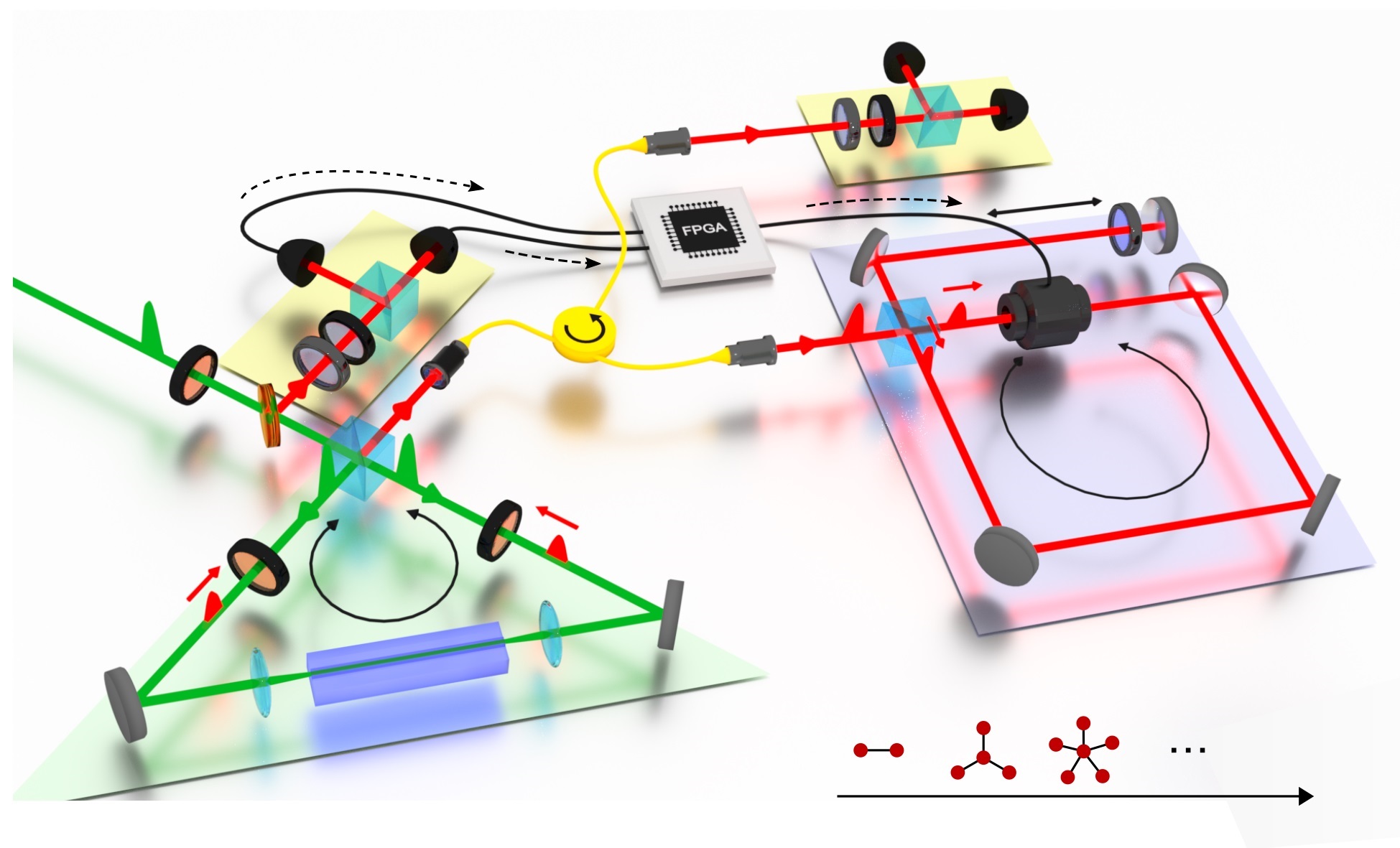
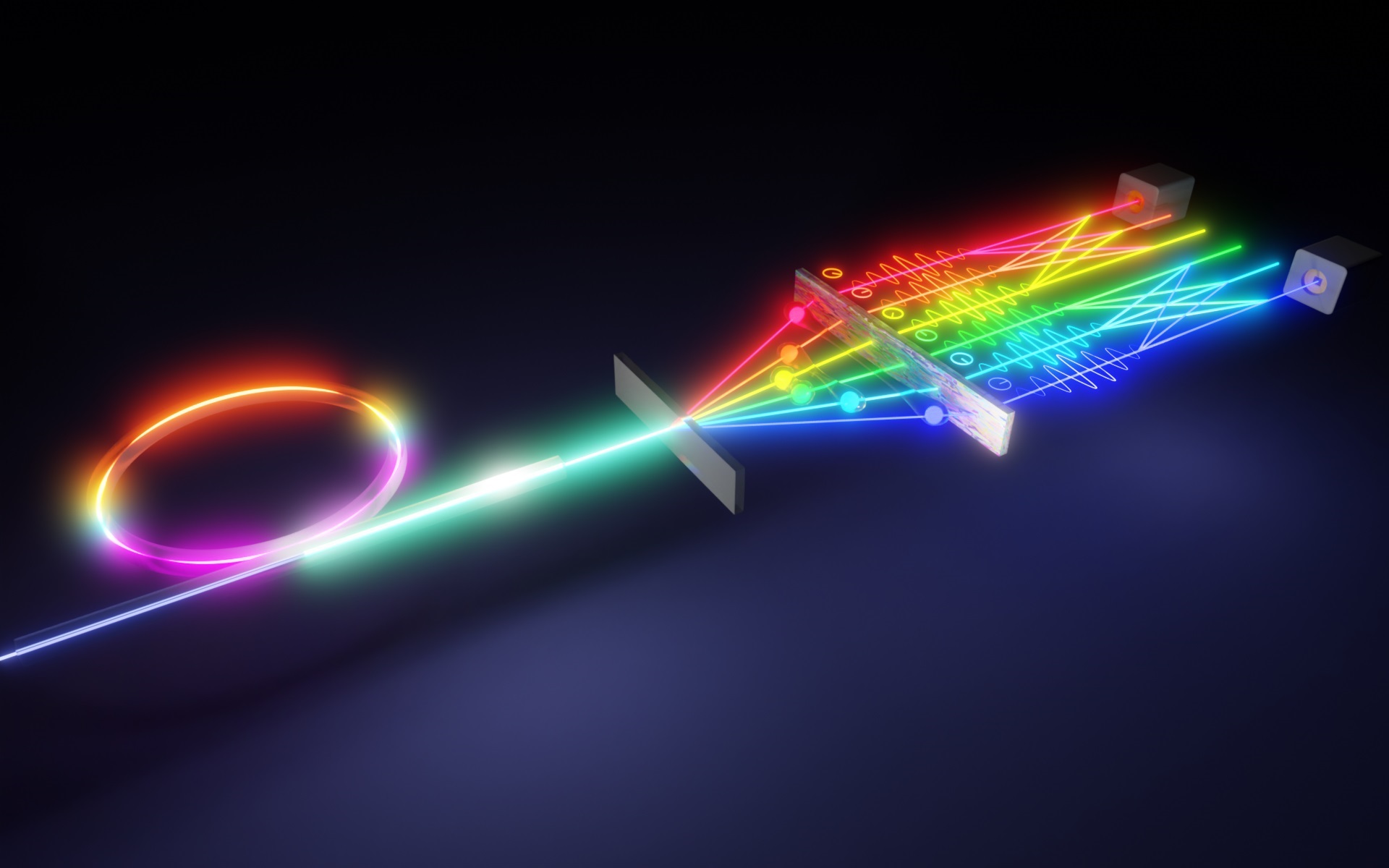
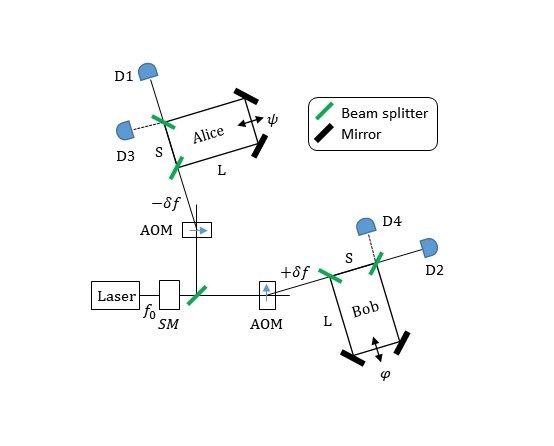
The team presents the first demonstration of the on-demand storage of orbital-angular-momentum states with weak coherent pulses at the single-photon-level in a rare-earth-ion doped crystal. Through the combination of this 3-dimensional spatial degree-of-freedom with 2-dimensional temporal and 2-dimensional spectral degrees of freedom, the team creates a multiple-DOF memory with high multimode capacity up to 3*2*2=12. This device can also serve as a quantum mode converter with high fidelity, which is the fundamental requirement for the construction of a multiplexed quantum repeater.
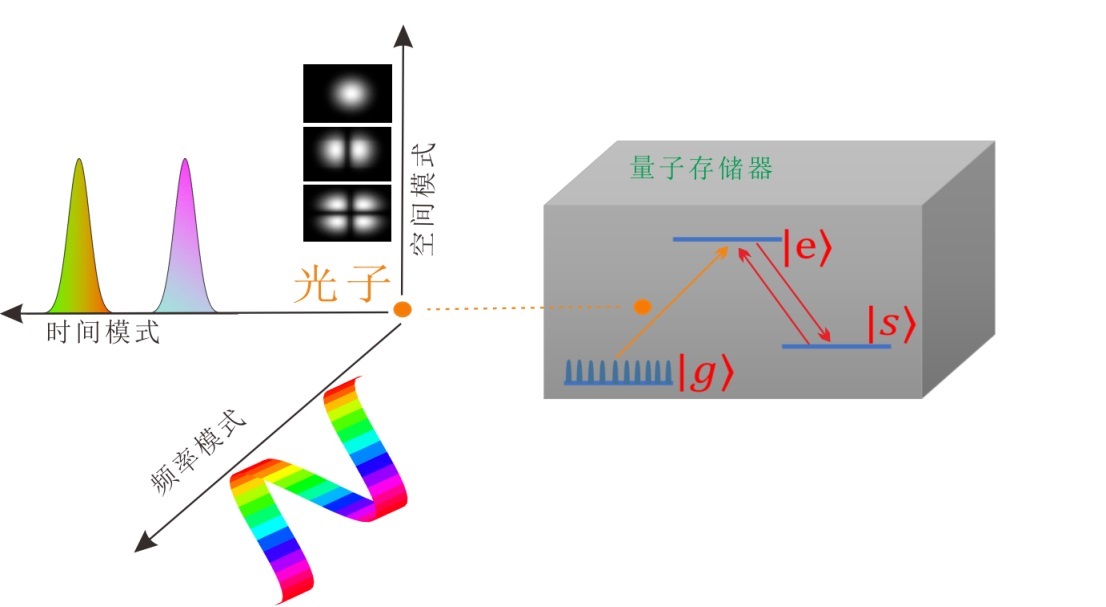
Multi-degree-of-freedom multiplexing quantum storage schematic (Image by YANG Tianshu)
The team further demonstrates that the device can perform arbitrary pulse operations within time and frequency DOF. Representative operations include pulses sequencer, multiplexer, selective spectral shifter and configurable beam splitter. The experimental results show that in all these operations, the three-dimensional quantum states carried by photons maintain a fidelity of about 89%.
This memory device can realize all the operations required for Knill-Laflamme-Milburn type quantum computatiom, and more applications are expected to be found in the field of linear optical quantum computing.
The work was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Collaborative Innovation Center for Quantum Information and Quantum Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
edited by GUO Jianjian, USTC News Center