21 September 2017
Nature Communications today published research by a team comprising Scottish and South African researchers, demonstrating entanglement swapping and teleportation of orbital angular momentum “patterns” of light. This is a crucial step towards realising a quantum repeater for high-dimensional entangled states.
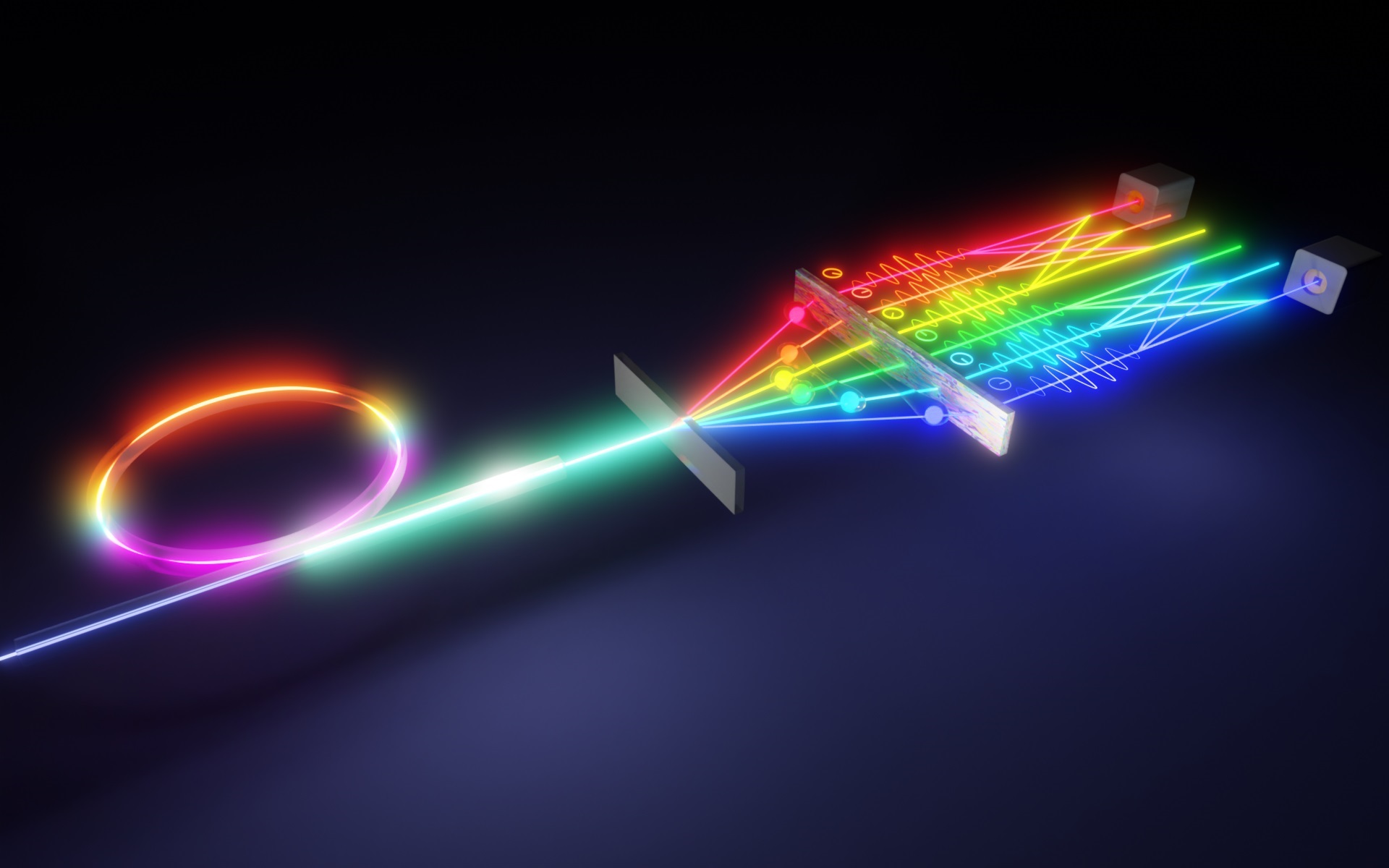
Quantum communication over long distances is integral to information security and has been demonstrated in free space and fibre with two-dimensional states, recently over distances exceeding 1200 km between satellites. But using only two states reduces the information capacity of the photons, so the link is secure but slow. To make it secure and fast requires a higher-dimensional alphabet, for example, using patterns of light, of which there are an infinite number. One such pattern set is the orbital angular momentum (OAM) of light. Increased bit rates can be achieved by using OAM as the carrier of information. However, such photon states decay when transmitted over long distances, for example, due to mode coupling in fibre or turbulence in free space, thus requiring a way to amplify the signal. Unfortunately such “amplification” is not allowed in the quantum world, but it is possible to create an analogy, called a quantum repeater, akin to optical fibre repeaters in classical optical networks.
An integral part of a quantum repeater is the ability to entangle two photons that have never interacted – a process referred to as “entanglement swapping”. This is accomplished by interfering two photons from independent entangled pairs, resulting in the remaining two photons becoming entangled. This allows the establishment of entanglement between two distant points without requiring one photon to travel the entire distance, thus reducing the effects of decay and loss. It also means that you don’t have to have a line of sight between the two places.
An outcome of this is that the information of one photon can be transferred to the other, a process called teleportation. Like in the science fiction series, Star Trek, where people are “beamed” from one place to another, information is “teleported” from one place to another. If two photons are entangled and you change a value on one of them, then other one automatically changes too. This happens even though the two photons are never connected and, in fact, are in two completely different places.
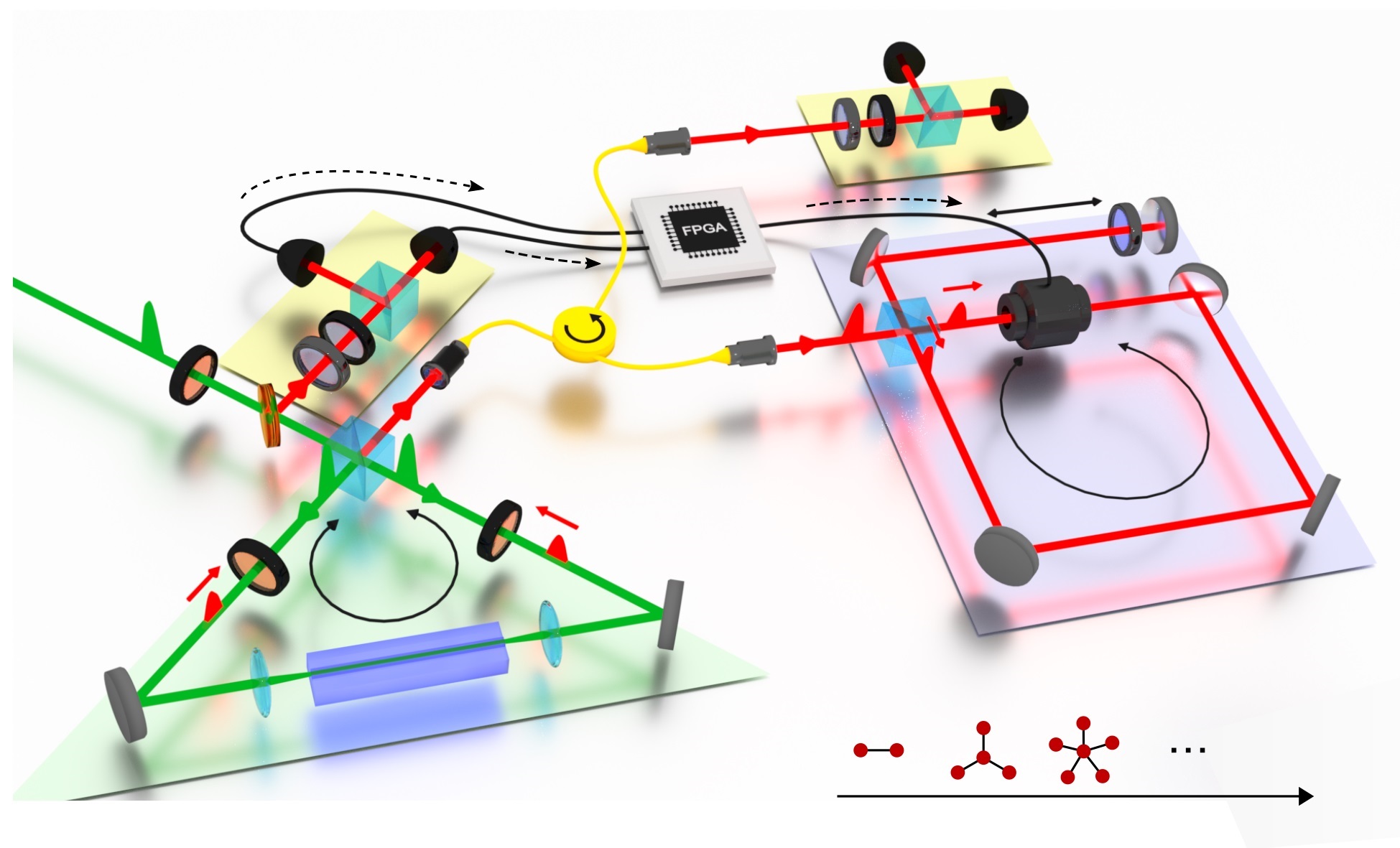
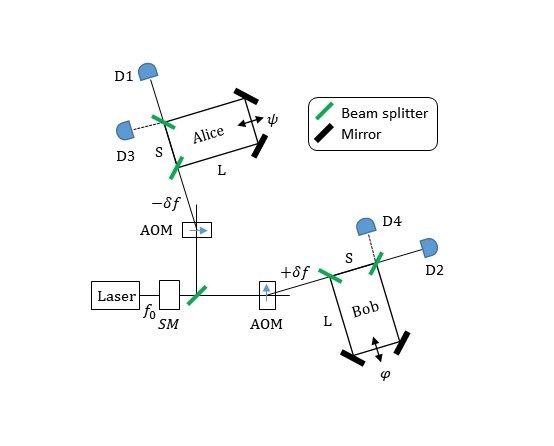
In this latest work, the team performed the first experimental demonstration of entanglement swapping and teleportation for orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light. They showed that quantum correlations could be established between previously independent photons, and that this could be used to send information across a virtual link. Importantly, the scheme is scalable to higher dimensions, paving the way for long-distance quantum communication with high information capacity.
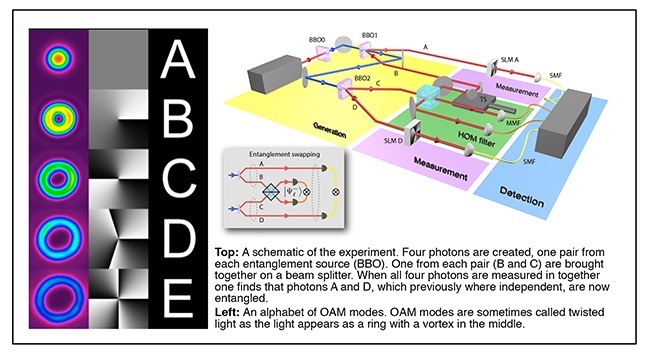
Background:
Present communication systems are very fast, but not fundamentally secure. To make them secure researchers use the laws of Nature for the encoding by exploiting the quirky properties of the quantum world. One such property is entanglement. When two particles are entangled they are connected in a spooky sense: a measurement on one immediately changes the state of the other no matter how far apart they are. Entanglement is one of the core resources needed to realise a quantum network.
Yet a secure quantum communication link over long distance is very challenging: Quantum links using patterns of light languish at short distances precisely because there is no way to protect the link against noise without detecting the photons, yet once they are detected their usefulness is destroyed. To overcome this one can have a repeating station at intermediate distances – this allows one to share information across a much longer distance without the need for the information to physically flow over that link. The core ingredient is to get independent photons to become entangled. While this has been demonstrated previously with two-dimensional states, in this work the team showed the first demonstration with OAM and in high-dimensional spaces.
Paper Abstract:
High-bit rate long distance quantum communication is an mooted technology for future communication networks and relies on high-dimensional quantum entanglement as a core resource. While it is known that spatial modes of light provide an avenue for high-dimensional entanglement, the ability to transport such quantum states robustly over long distances remains challenging. To overcome this, entanglement swapping may be used to generate remote quantum correlations between particles that have not interacted, the core ingredient of a quantum repeater, akin to repeaters in optical fibre networks. Here we demonstrate entanglement swapping of multiple orbital angular momentum states of light. Our approach does not distinguish between different anti-symmetric states, and thus entanglement swapping occurs for several thousand pairs of spatial light modes simultaneously. This work represents the first step towards a quantum network for high-dimensional entangled states and provides a test bed for fundamental tests of quantum science.