Jul 17, 2013
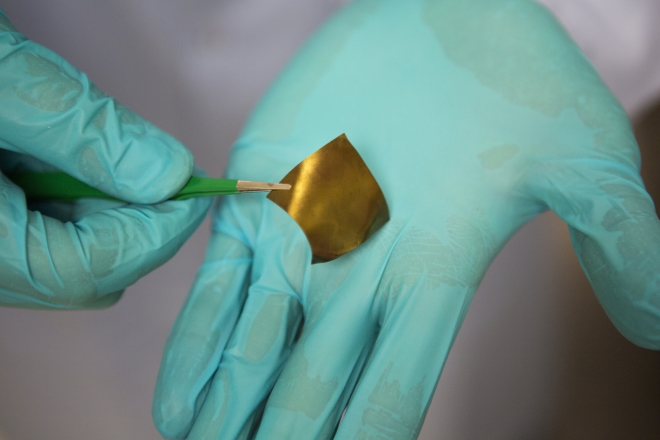
ANN ARBOR—Networks of spherical nanoparticles embedded in elastic materials may make the best stretchy conductors yet, engineering researchers at the University of Michigan have discovered.
Flexible electronics have a wide variety of possibilities, from bendable displays and batteries to medical implants that move with the body.
"Essentially the new nanoparticle materials behave as elastic metals," said Nicholas Kotov, the Joseph B. and Florence V. Cejka Professor of Engineering. "It's just the start of a new family of materials that can be made from a large variety of nanoparticles for a wide range of applications."
Finding good conductors that still work when pulled to twice their length is a tall order—researchers have tried wires in tortuous zigzag or spring-like patterns, liquid metals, nanowire networks and more. The team was surprised that spherical gold nanoparticles embedded in polyurethane could outcompete the best of these in stretchability and concentration of electrons.
"We found that nanoparticles aligned into chain form when stretching. That can make excellent conducting pathways," said Yoonseob Kim, first author of the study to be published in Nature on July 18 and a graduate student in the Kotov lab in chemical engineering.
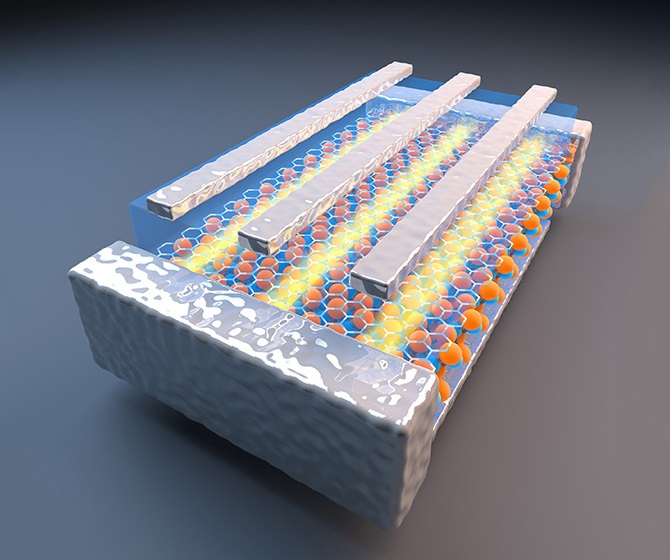
To find out what happened as the material stretched, the team took state-of-the-art electron microscope images of the materials at various tensions. The nanoparticles started out dispersed, but under strain, they could filter through the minuscule gaps in the polyurethane, connecting in chains as they would in a solution.
"As we stretch, they rearrange themselves to maintain the conductivity, and this is the reason why we got the amazing combination of stretchability and electrical conductivity," Kotov said.
The team made two versions of their material—by building it in alternating layers or filtering a liquid containing polyurethane and nanoparticle clumps to leave behind a mixed layer. Overall, the layer-by-layer material design is more conductive while the filtered method makes for extremely supple materials. Without stretching, the layer-by-layer material with five gold layers has a conductance of 11,000 Siemens per centimeter (S/cm), on par with mercury, while five layers of the filtered material came in at 1,800 S/cm, more akin to good plastic conductors.
The eerie, blood-vessel-like web of nanoparticles emerged in both materials upon stretching and disappeared when the materials relaxed. Even when close to its breaking point, at a little more than twice its original length, the layer-by-layer material still conducted at 2,400 S/cm. Pulled to an unprecedented 5.8 times its original length, the filtered material had an electrical conductance of 35 S/cm—enough for some devices.
Kotov and Kim chiefly see their stretchable conductors as electrodes. Brain implants are of particular interest to Kotov.
"They can alleviate a lot of diseases—for instance, severe depression, Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease," he said. "They can also serve as a part of artificial limbs and other prosthetic devices controlled by the brain."
Rigid electrodes create scar tissue that prevents the electrode from working over time, but electrodes that move like brain tissue could avoid damaging cells, Kotov said.
"The stretchability is essential during implantation process and long-term operation of the implant when strain on the material can be particularly large," he said.
Whether in the brain, heart or other organs—or used for measurements on the skin—these electrodes could be as pliable as the surrounding tissue. They could also be used in displays that can roll up or in the joints of lifelike "soft" robots.
Because the chain-forming tendency of nanoparticles is so universal many other materials could stretch, such as semiconductors. In addition to serving as flexible transistors for computing, elastic semiconductors may extend the lives of lithium-ion batteries. Kotov's team is exploring various nanoparticle fillers for stretchable electronics, including less expensive metals and semiconductors.
Kotov is a professor of chemical engineering, biomedical engineering, materials science and engineering and macromolecular science and engineering.
The study is titled "Stretchable Nanoparticle Conductors with Self-Organized Conductive Pathways." The work is funded by the STX foundation in Seoul, South Korea; U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science; Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency; Air Force Office of Scientific Research; and National Science Foundation. U-M is pursuing patent protection for the intellectual property and seeking commercialization partners to help bring the technology to market.