25 August 2015
Nanomaterials have the potential to play a central role in solving many of today’s biggest sustainability issues, whether it’s developing more efficient renewable energy technologies, removing pollutants from the air and water, or even in the treatment of diseases. Key to the success of nanomaterials in these areas is the development of scalable production methods that can precisely control the properties of these materials.
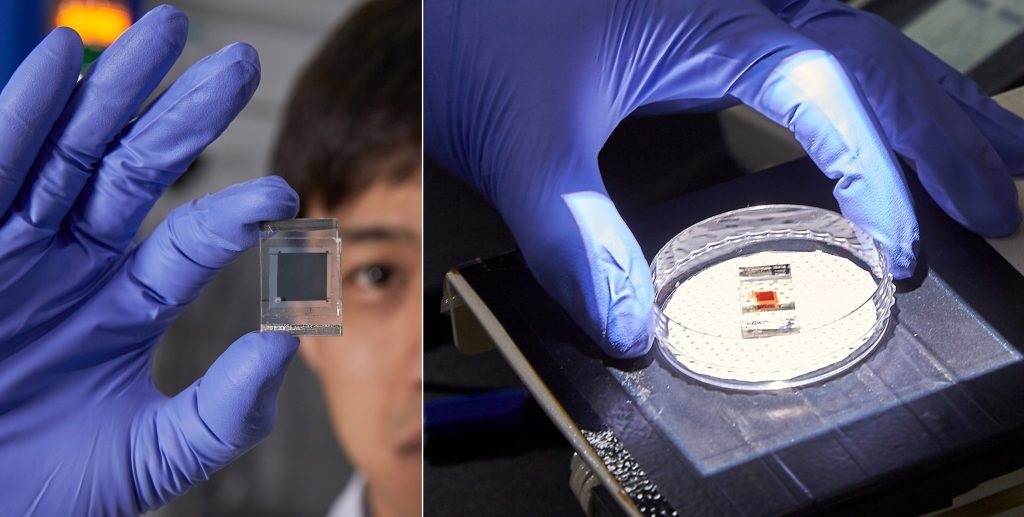
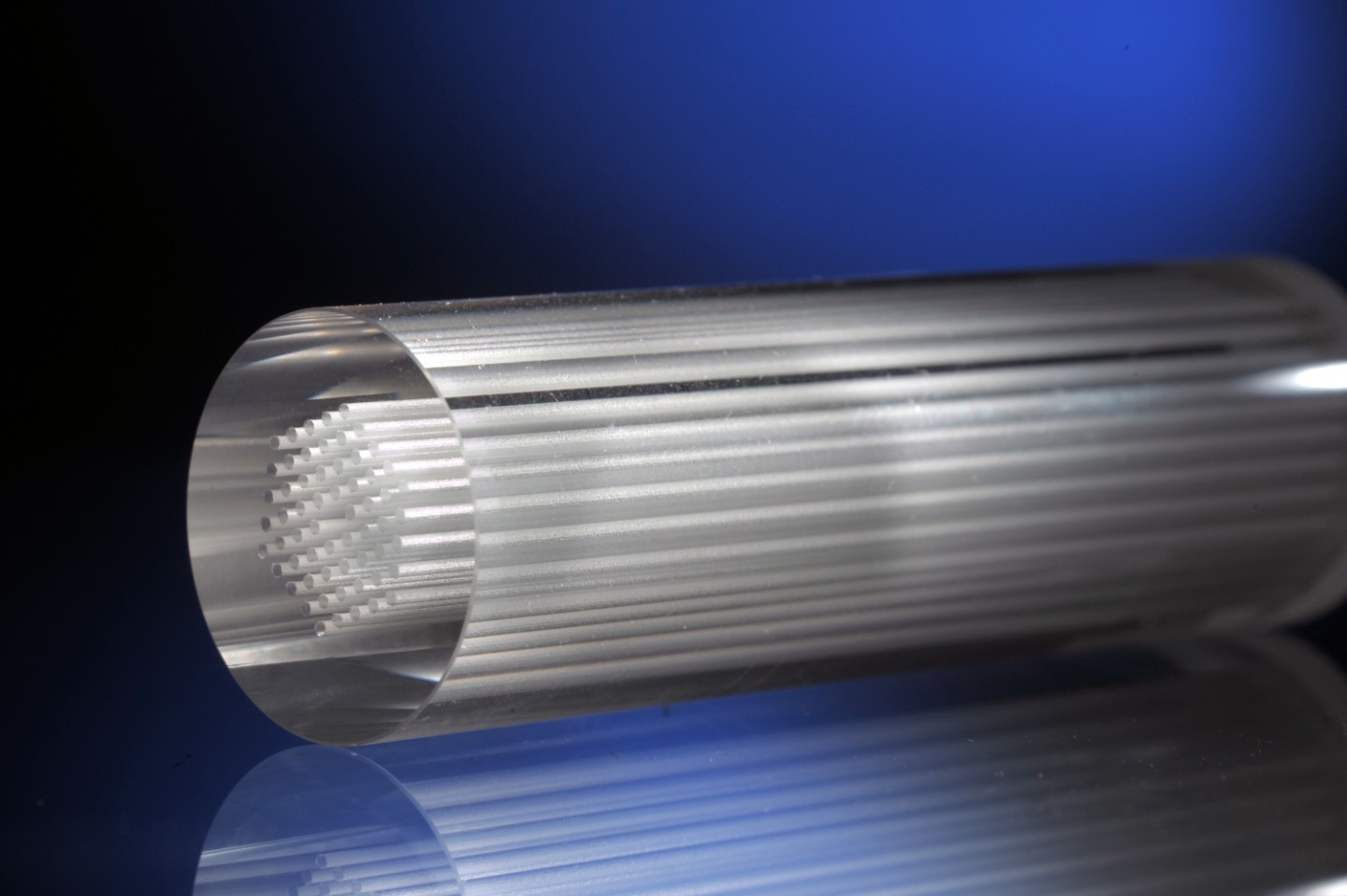
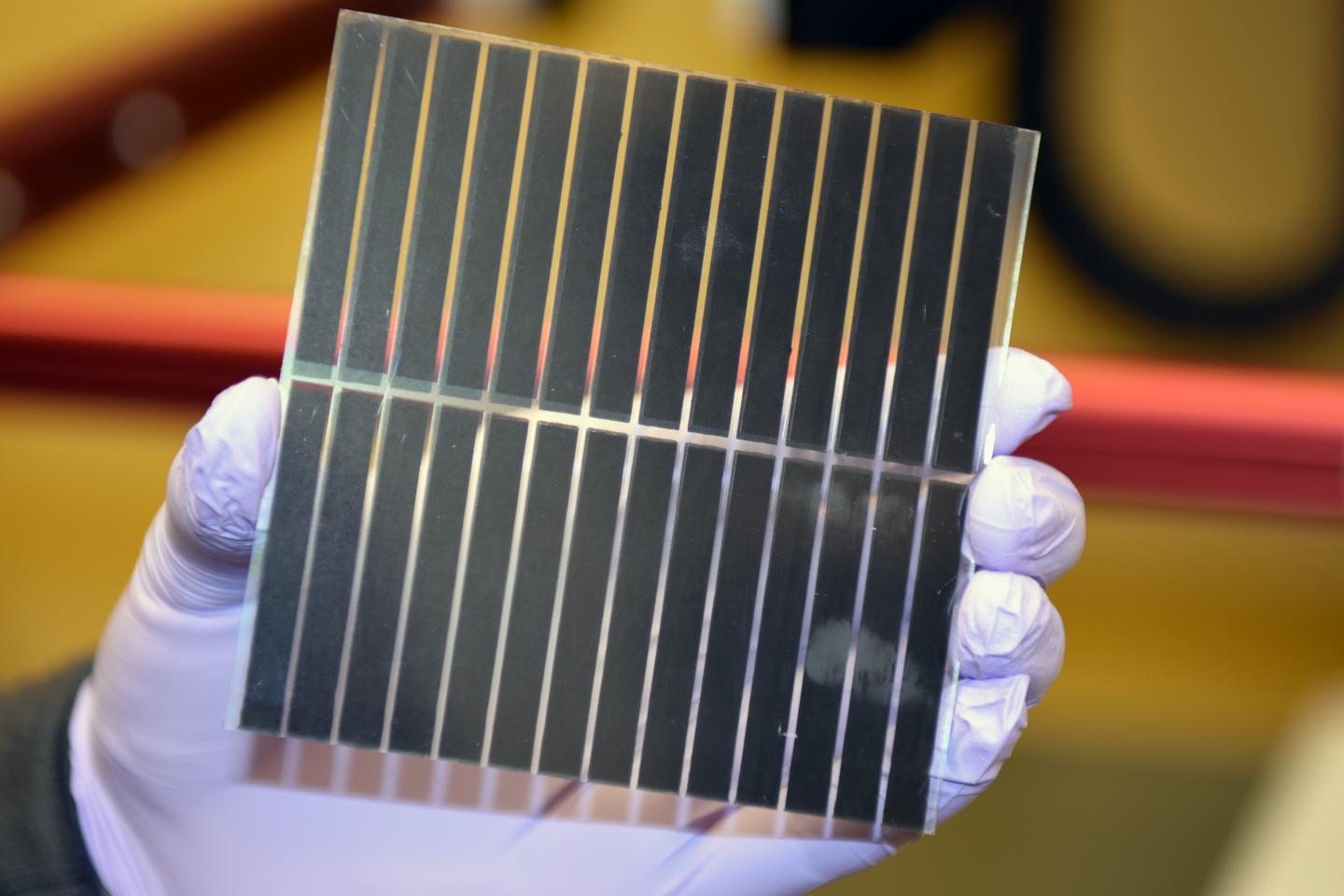
CSCT student, David Miles has published a paper that demonstrates the rapid and scalable production of Zinc Oxide nanomaterials using a technique called electrochemical anodization. The technique can be controlled to give rise to a wide range of interesting structures, with different sizes and shapes, which can be tailored towards specific applications.
Working with Dr Davide Mattia, Dr Petra Cameron and collaborators at Yonsei University, David is currently applying these nanomaterials within photovoltaic cells where their unique properties can be used to enhance the efficiency of these devices.
Read the full paper in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A where the paper is also featured on the front cover.

Designing bespoke nanomaterials for energy applications
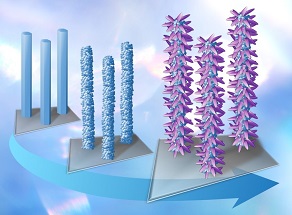
3D hierarchical structures