17 DECEMBER 2019
A new design of optical chips enables light to experience multiple dimensions, which could underpin versatile platforms for advanced communications and ultra-fast artificial intelligence technologies.
This scientific breakthrough was led jointly by The Australian National University (ANU) and the University of Rostock in Germany, with other collaborators in Germany, the University of Central Florida in the US and UNSW Canberra.
"Light can evolve in up to seven dimensions on our specially designed circuits, which is mind boggling when you realise that the space around us is three-dimensional," said Professor Andrey Sukhorukov, who led the development of new theoretical concepts with a team of scientists at the Nonlinear Physics Centre of the ANU Research School of Physics.
Professor Alexander Szameit from the University of Rostock led the experimental work, including the cutting-edge fabrication of optical circuits.
"Making use of higher dimensions on optical chips could support a variety of future technologies that involve machine learning and performing complex tasks autonomously," Professor Szameit said.
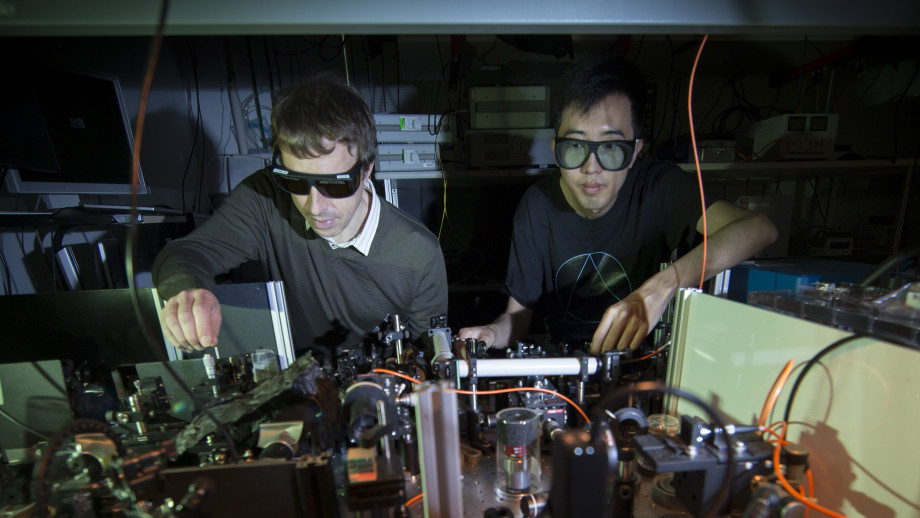
Professor Andrey Sukhorukov (left) and Dr Kai Wang (right) at The Australian National University. Image credit: ANU
Dr Kai Wang, who worked on the key aspects of the project at ANU, said enabling light to travel beyond our three-dimensional space is a major breakthrough, and would drastically enhance the capability of today's optical chips.
"High-dimensional network structures can be found in human brains - if optical circuits can emulate this, their computation capability will also be boosted dramatically," Dr Wang said.
"This takes us into the realm of science fiction, which I think is really exciting. The sky is the limit in terms of potential future applications that could build on our discovery."
Lukas Maczewsky, a PhD scholar who performed the experiments at University of Rostock, said the team's innovation can be used to develop optical switches and sensors that can respond very sharply to transmit or block light.
"Our work is an important step towards creating an ultra-compact and energy-efficient platform for optical networks," Mr Maczewsky said.
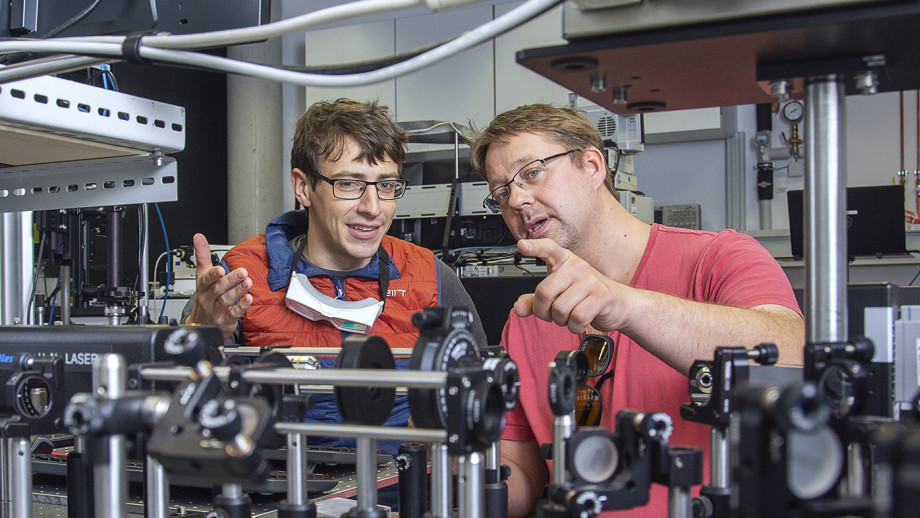
Mr Lukas Maczewsky (left) and Professor Alexander Szameit (right) at the University of Rostock, Germany. Image credit: University of Rostock
"Light can travel inside the circuits on an optical chip but, on a mass-scale, circuits are most efficiently made within one plane - just like roads without overpasses. Without the need to build overpasses on planar circuits, we make better use of the cross-talks of light between neighbouring pathways to engineer the behaviour of light."
The research is published in Nature Photonics:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-019-0562-8