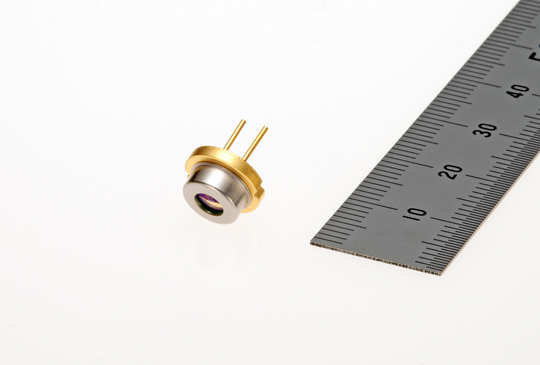
TOKYO, Decemember 14, 2016 - Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (TOKYO: 6503) announced today that it will launch a new continuous-wave (CW) laser diode (LD), the ML562G85, offering a world-record output power of 2.1W and a brilliant 639-nanometer(nm) red light for projectors on February 1, 2017. The LD's pure red color and low power consumption are expected to be adopted for large-venue laser-based projectors requiring high brightness.
It has been a technical challenge to produce red LDs offering high output at high temperature using a lasing wavelength not exceeding 640 nm, the preferred maximum for achieving necessary luminosity. Mitsubishi Electric succeeded in developing its new CW high-power red LD that operates at high temperature by using original high-power technology, including an optimized LD structure.
Product Features
1) 2.1W output power in CW and brilliant 639-nm red light
- Optimized epitaxial structure and emitter size enables world-record 2.1W output (CW), 4.2 times greater than that of the company's current model
- High-luminosity 639-nm laser light and 2.1W output (CW) produce 250 lumens per LD
- High wall-plug efficiency of 41 percent at 2.1W (CW) and low case temperature of 25 degrees Celsius help to reduce projector power consumption
2) Widest operating temperature range for a red LD thanks to improved heat dissipation
- Large 9.0-mm-diameter transistor-outline can (TO-CAN) package improves heat dissipation
- Unprecedented operating temperature range of 0 to 45 degrees Celsius at 2.1W (CW), compared to the current model's range of 0 to 40 degrees Celsius at 0.5W (CW)
Currently, light sources used for projectors are shifting from mercury lamps to solid-state lights, which offer advantages such as high wall-plug efficiency, wide co lor gamut and extra-reliable operation. LDs, which are especially efficient compared to other solid-state lights, can help projectors to achieve low power consumption. Also, only LDs can emit pure-color light in a wide power range to enable a projector to realize a wide color gamut (ITU-R BT.2020 compliant) and high dynamic range. LDs are drawing much attention as the likely light source for advanced projectors.
There are two types of LD light sources for projectors—CW and pulsed. In November 2010, Mitsubishi Electric launched its high-power-red LD (ML501P73), which offers output of 1.0W (pulse) or 0.5W (CW) for its 638-nm light. The LD incorporates original epitaxial growth technology and window-mirror structure. Also, the ML562G84 launched in September 2015 achieves 2.5W of power for its 638-nm light in pulse operation.