10 July 2013
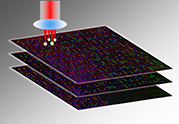
Using nanostructured glass, scientists at the University of Southampton have, for the first time, experimentally demonstrated the recording and retrieval processes of five dimensional digital data by femtosecond laser writing. The storage allows unprecedented parameters including 360 TB/disc data capacity, thermal stability up to 1000°C and practically unlimited lifetime.
Coined as the ‘Superman’ memory crystal, as the glass memory has been compared to the “memory crystals” used in the Superman films, the data is recorded via self-assembled nanostructures created in fused quartz, which is able to store vast quantities of data for over a million years. The information encoding is realised in five dimensions: the size and orientation in addition to the three dimensional position of these nanostructures.
A 300 kb digital copy of a text file was successfully recorded in 5D using ultrafast laser, producing extremely short and intense pulses of light. The file is written in three layers of nanostructured dots separated by five micrometres (one millionth of a metre).
The self-assembled nanostructures change the way light travels through glass, modifying polarisation of light that can then be read by combination of optical microscope and a polariser, similar to that found in Polaroid sunglasses.
The research is led by Jingyu Zhang from the University’s Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) and conducted under a joint project with Eindhoven University of Technology.
“We are developing a very stable and safe form of portable memory using glass, which could be highly useful for organisations with big archives. At the moment companies have to back up their archives every five to ten years because hard-drive memory has a relatively short lifespan,” says Jingyu.
“Museums who want to preserve information or places like the national archives where they have huge numbers of documents, would really benefit.”
The Physical Optics group from the ORC presented their ground-breaking paper at the photonics industry's renowned Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO’13) in San Jose. The paper, ‘5D Data Storage by Ultrafast Laser Nanostructuring in Glass’ was presented by the during CLEO's prestigious post deadline session.
This work was done in the framework of EU project Femtoprint http://www.femtoprint.eu
Professor Peter Kazansky, the ORC’s group supervisor, adds: “It is thrilling to think that we have created the first document which will likely survive the human race. This technology can secure the last evidence of civilisation: all we’ve learnt will not be forgotten.”
The team are now looking for industry partners to commercialise this ground-breaking new technology.
The Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) is one of the world’s leading institutes for photonics research based at the University of Southampton. Over the last 40 years, the group has contributed significantly to the growth of the photonics industry.
The University of Southampton is a leading UK teaching and research institution with a global reputation for leading-edge research and scholarship across a wide range of subjects in engineering, science, social sciences, health and humanities.
With over 23,000 students, around 5000 staff, and an annual turnover well in excess of £435 million, the University of Southampton is acknowledged as one of the country's top institutions for engineering, computer science and medicine. We combine academic excellence with an innovative and entrepreneurial approach to research, supporting a culture that engages and challenges students and staff in their pursuit of learning.
The University is also home to a number of world-leading research centres including the Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, the Optoelectronics Research Centre, the Institute for Life Sciences, the Web Science Trust and Doctoral training Centre, the Centre for the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease, the Southampton Statistical Sciences Research Institute and is a partner of the National Oceanography Centre at the Southampton waterfront campus.
Download the paper
5D Data Storage by Ultrafast Laser Nanostructuring in Glass