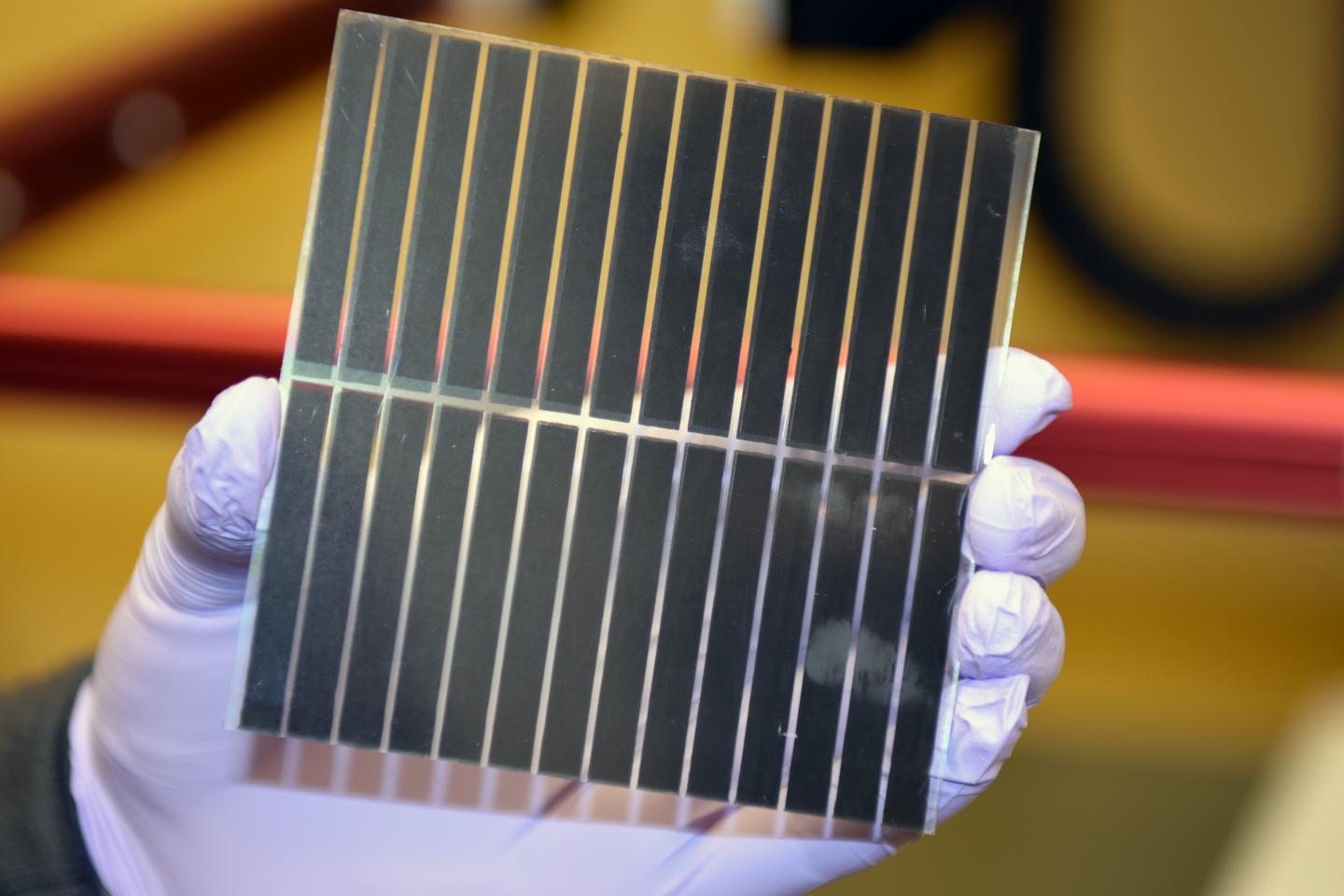
Neuchâtel, 19 February 2014 – The Meyer Burger Group and CSEM, with support from the Swiss Federal Office of Energy and of the Canton of Neuchâtel, will strengthen Switzerland’s position as leader for technological innovation in the photovoltaic sector and ensure its competitiveness as a major equipment provider in the international photovoltaic industry. The key is called heterojunction silicon technology.
More than 37 Gigawatt peak (GWp) of photovoltaic (PV) output was installed in 2013 with a cumulative global output by the end of 2013 of approximately 140 GWp which lead to a major expansion in electrical energy in Europe. Photovoltaics will contribute significantly to the future global energy mix. Increasingly efficient modules and competitive technologies are making photovoltaic more economically viable while achieving lowest cost of energy (CHF/kWh).
Against this background, the Swiss-Inno HJT project is supported by the Federal Office of Energy, industrial partners and the Canton of Neuchâtel for a total cost amounts to about 10 million Swiss Francs over 3 years .This grant promotes the setup of a pilot production system for high-efficiency cells with the goal of producing photovoltaic energy at lowest prices while illustrating the superiority of this innovative heterojunction technology in a demo system.
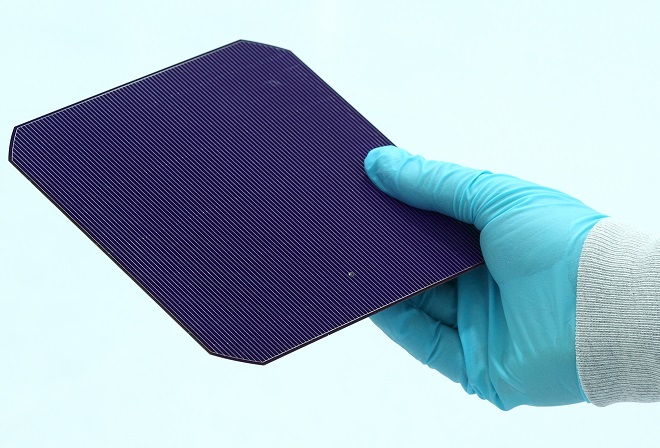
Heterojunction silicon technology (HJT) consists of ultra-thin (several thousandths of a micrometer) layers of amorphous silicon in the nanometer range that have been deposited on both sides of mono crystalline silicon wafers. The level of efficiency is higher than in standard cells with the production process actually requiring fewer steps. Additional advantages of the HJT technology is it remarkable temperature characteristics and it bi-faciality which can lead to increased energy efficiency (kWh/Wp). This is the basis of decreased energy costs (CHF/KwH). HJT technology also paves the way for low cost mass production of PV modules (less than 0.6 CHF/Wp). Development of the technology started in 2008 in a partnership between Roth and Rau, the competence centre for coating technologies within the Meyer Burger Group, and the Photovoltaics Laboratory of the IMT at EPFL.
Enormous export opportunities for Swiss industry
The heart of the Swiss-Inno HJT project is the development of an innovative pilot production line for heterojunction cells and modules while continuously improving and optimising the production process. Important goal for the project are the successful market entry of the HJT technology as well as the realisation of promising export opportunities. The successful market entry of HJT is expected to contribute to further price reductions for PV power systems in general and to significantly lower the overall cost of solar energy production. Heterojunction silicon technology is especially suitable for energy efficient roof installations and building integrations and could therefore become a preferred technology for Swiss domestic market applications. This will support the federal energy strategy 2050 which targets an increased share of renewable electricity in the future energy mix.
Several Swiss technology centers such as Meyer Burger group members Roth & Rau Research PASAN and the Meyer Burger competence centre in Thun as well as CSEM’s PV-Center, are joining forces and combining in their respective expertise to demonstrate HJT technology for the industrial production of advanced solar cells and modules. After the project is completed, the pilot lines will be key research and development platforms to bring further innovations in PV technology to maturity close to industrial production conditions in order to maintain a competitive edge.