Feb.25, 2019
The potential computing revolution that quantum computers have long promised is based on their weird property called superposition. Namely, qubits can take both logical states 0 and 1 simultaneously, on top of any value in between. By mastering superpositions of the whole quantum memory, quantum computers can quickly solve problems that would require too much computing time from regular computers working with simply 0s and 1s.
However, qubits are sensitive, and currently hold quantum information for less than a millisecond at a time, even when kept frozen at temperatures colder than the dark side of the moon. To extract any useful information, the method that reads information from qubits must take the least amount of time as possible, allowing as few errors as possible.
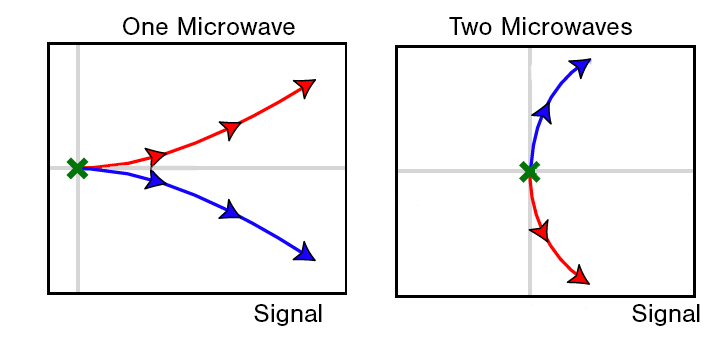
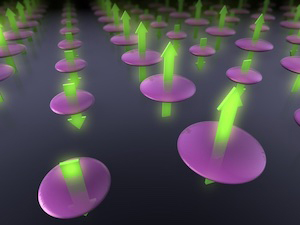
The two quantum states, here represented by red and blue arrows, separate faster and can be read quicker when the system is pulsed with two microwaves. Figure credit: Joni Ikonen.
Joni Ikonen, a PhD student at Aalto University, has developed a new method that helps do just that. Until now, the method used to read information from a qubit was to apply a short microwave pulse to the superconducting circuit containing the qubit and then measure the reflected microwave. After 300 nanoseconds, the state of the qubit can be deduced from the behavior of the reflected signal.
The new method applies an extra microwave pulse at the same time to the qubit itself, as well as to the circuit attached to the qubit. By using two pulses instead of one, the team at Aalto was able to make the reflected pulse reveal qubit states substantially faster than when they only applied a single pulse.
‘We were able to complete the readout in 300 nanoseconds in our first experiments, but we think that going below 100 nanoseconds is just around the corner,’ says Joni Ikonen.
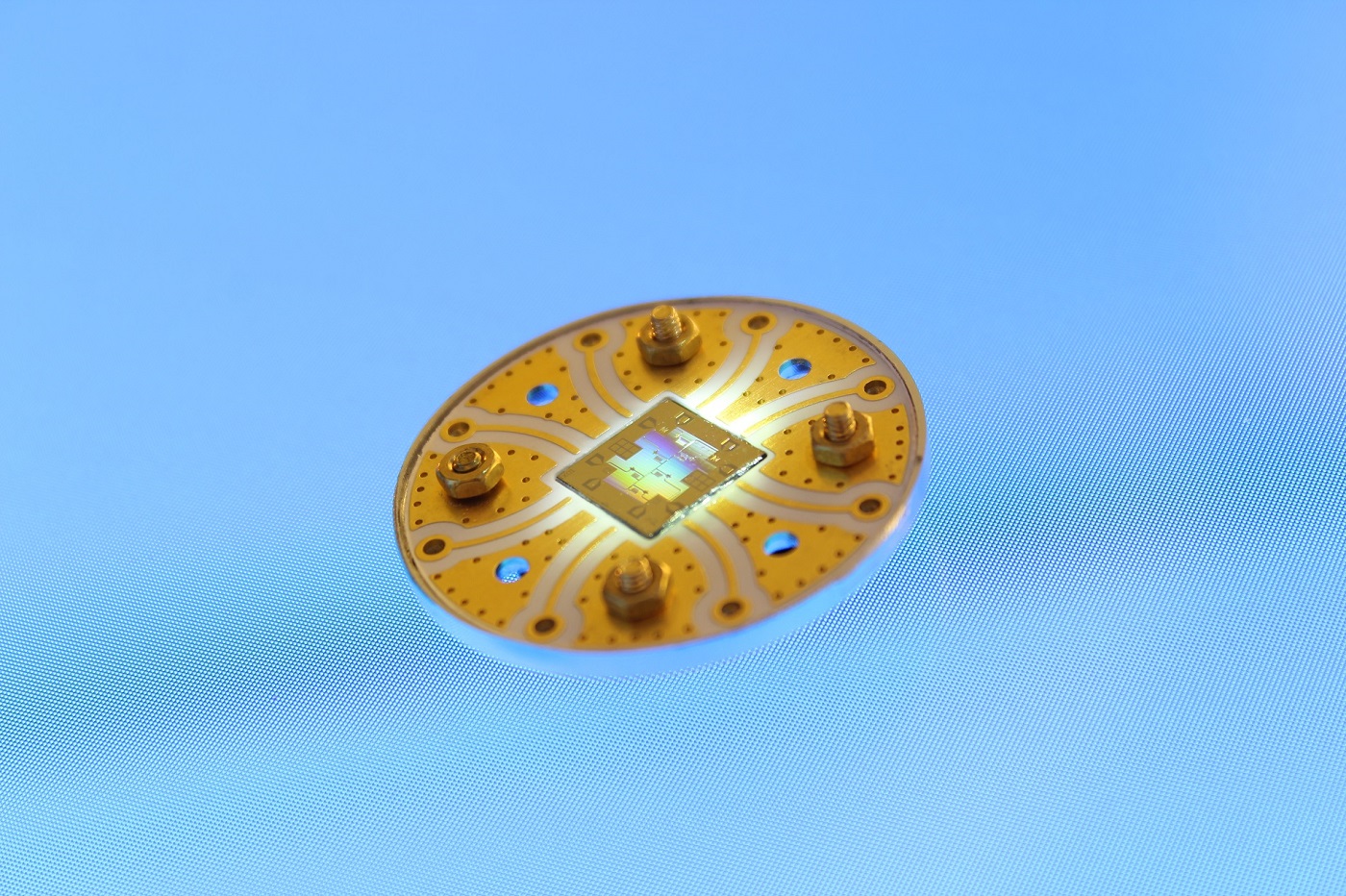
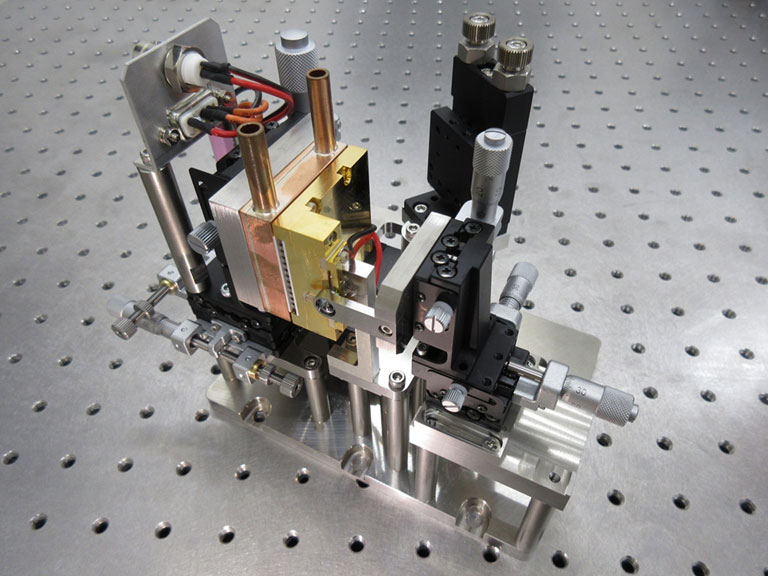
Quantum chip mounted on a sample holder. Figure credit: Jan Goetz.
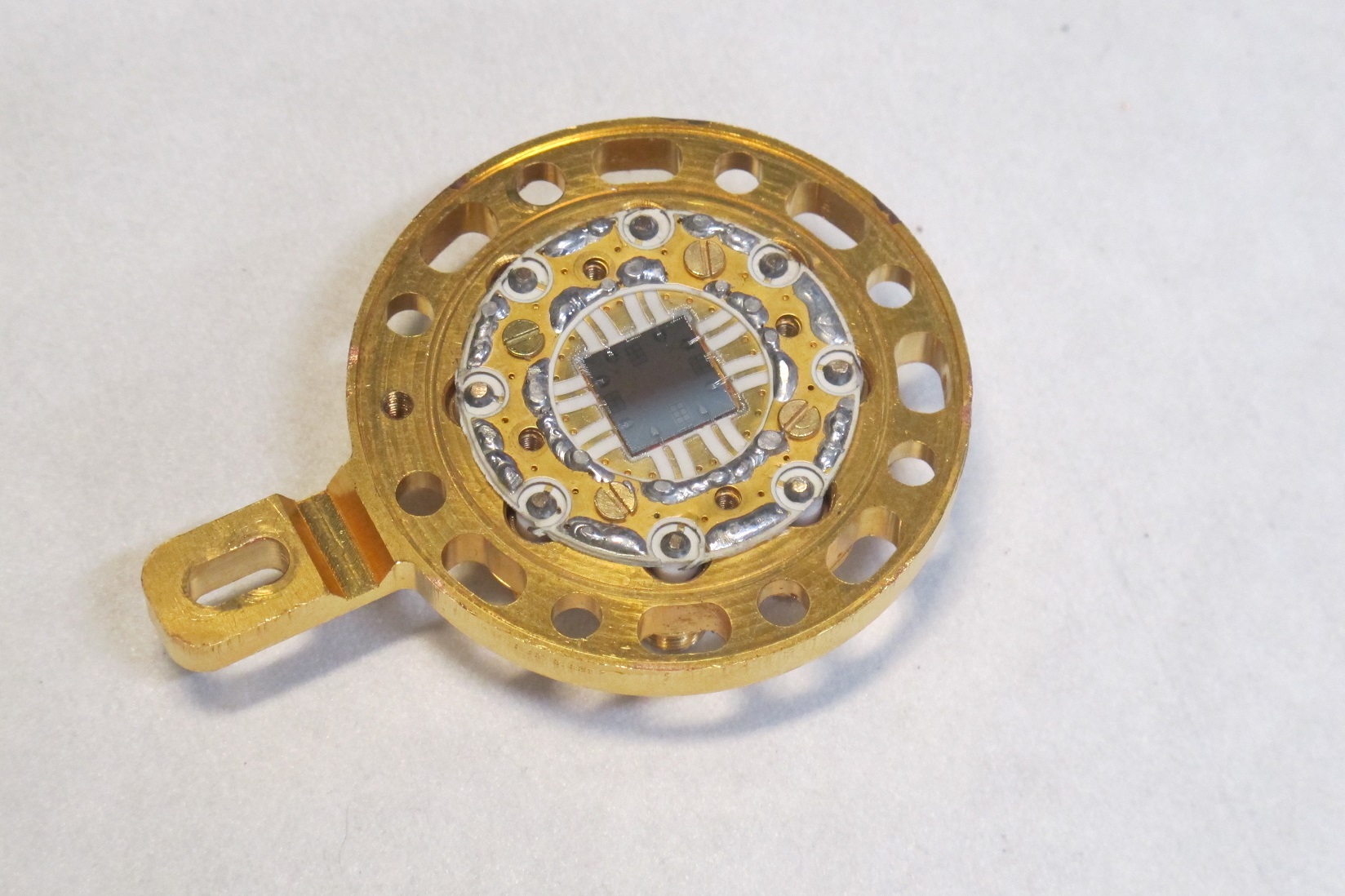
Quantum chip mounted on a sample holder. Figure credit: Aalto University.
By improving the speed and accuracy of the information retrieved from qubits, scientists may be able to move closer to realising the promise of useful quantum computing.
‘This is an amazing result in getting the slippery qubits in order. I hope that it will help the community in the future to reach quantum supremacy and error correction, the path to a quantum computer of practical value,’ says Dr. Möttönen, who co-supervised the work with Dr. Jan Goetz.
Jan Goetz (left), Joni Ikonen (middle), and Mikko Möttönen (right). Figure credit: Aalto University.
Scientific article (to be cited in stories on this research): Joni Ikonen, Jan Goetz, Jesper Ilves, Aarne Keränen, Andras M. Gunyho, Matti Partanen, Kuan Y. Tan, Leif Grönberg, Visa Vesterinen, Slawomir Simbierowicz, Juha Hassel, and Mikko Möttönen, Qubit Measurement by Multi-Channel Driving, Physical Review Letters 122, 080503 (2019).
Link to the article: